HS-ACC
HS-ACC SDSCoal-Based Activated Carbon

What is HS-ACC
Hydrosil’s HS-ACC is a highly active granular activated carbon (GAC) manufactured from select grades of coal. Hydrosil’s HS-ACC is designed for liquid phase applications. The coal-based carbon is typically used in portable water purification, wastewater treatment, industrial air purification, chemical purification, and the food and beverage industry. Coal-based activated carbon is known best for its’ combination of micro, meso, and macro pore structure. With a variety of pore structure the material is capable of removing a wide range of molecular weights.
HS-ACC is NSF/ANSI/CAN 61 certified for potable water use.
Where is HS-ACC Used
HS-ACC is commonly used in oil and gas refineries, municipal drinking water purification, and industrial pollution control. Industrial projects that use HS-ACC include groundwater treatment, stormwater run-off treatment, reverse osmosis systems, and removal of dissolved organics.
HS-ACC, coal based activated carbon, is being used in combination with HS-PF for removal of per- and poly-fluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS). Granular activated carbon is one of the most well known technologies for removal of PFAS compounds through adsorption.
What is Activated Carbon
Activated carbon commonly referred to as activated charcoal is a a highly porous material used to remove pollutants from contaminated liquid and gas streams. Activated carbon is derived from a variety of raw materials such as coconut, wood, coal (bituminous, anthracite, sub-bituminous, and lignite), peat, and bamboo. Each raw material has unique properties which effect the resulting pore structure, carbon content, and ash content, which are important characteristics when removing a contaminant of concern. The material is used in remediation, medical, and industrial applications where adsorption is required. Activated carbon has strong physical adsorption properties known as London Dispersion Forces which is a Van der Waals Force. The attraction between the activated carbon and the pollutant are highly dependent on the vapour pressure of the adsorbing molecules. Activated carbon is often altered or impregnated by chemicals to enhance the surface area of the carbon. When the carbon is chemically altered the bonds are much stronger than London Dispersion Forces. Chemicals often impregnated on activated carbon include potassium hydroxide, phosphoric acid, or sulfur. With the addition of chemicals the activated carbon will have an affinity for select compounds such acidic or basic pollutants.
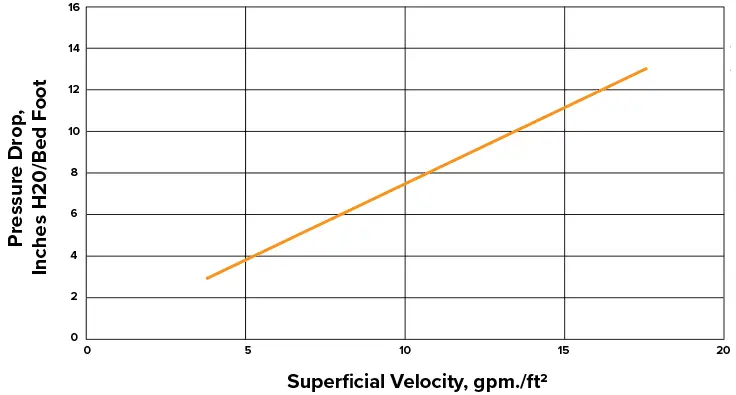
Pressure Drop
Typical Physical Properties
| Property: | Value: |
| Iodine Number, mg/gm | 1100 - 1200 |
| Apparent Density, lb/ft3 | 29-31 |
| U.S. Standard Sieve Size (Mesh Size) | 12 x 40 |
| Butane Number, % ww | 23.5 (60 CTC) |
| Hardness, Min. (ASTM D-3802) | 98 |
| Total Surface Area (BET), m2/gm | 1150 – 1250 |
| Ash, Max (ASTM D-2866) | 3% |
- Air
- Water
- PFAS
- Sediment
Common Applications:
- Various Hydrocarbons
- Low Molecular Weight Hydrocarbons
- Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA)
- Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOA)
- Perfluoroalkyl Sulfonic Acids and Sulfonates (PFSA)
- Fluorotelomer Carboxylic Acids (FTCA)
- Per- Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS)